General |
| Crystallization Methods |
1. Microbatch |
|
2. Sitting Drop |
|
3. Hanging Drop |
|
4. Lipidic Cubic Phase |
| Ambient temperature |
4 to 30°C |
| Computer requirement |
PC with Windows 11, 10, 8 or 7 |
Vapor Diffusion Method
|
| Volume of droplet |
0.1 + 0.1 to 8.0 + 8.0 microliters |
| Plates accommodated |
All high quality plates and hanging drop cover slides can be used |
| Number of wells dispensed |
1 to 96x5 |
Microbatch Method
|
| Volume range of crystallization trial |
0.1 + 0.1 to 8.0 + 8.0 microliters |
| Typical volume of crystallization trial for
screening. |
0.1 + 0.1 to 0.3 + 0.3 microliters |
| Typical volume of crystallization trial for
optimization |
0.6 to 2.0 microliters (Oryx8 only) |
| Volume of protein dispensed per trial |
0.1 to 5 microliters |
| Number of crystallization trials set up per run |
1 to 384 (or more) |
| Number of solutions dispensed in each trial for optimization |
1 to 7 (including water) |
| Plates accommodated |
All high quality plates can be used |
Lipidic Cubic Phase
|
| Volume range of Lipidic Cubic Phase |
10 nL to 1.0 microliters or larger |
| Plates accommodated |
All high quality sandwich or sitting drop plates can be used |
| Number of wells dispensed |
1 to 96x5 |
| Number of solutions dispensed in each trial for optimization |
1 to 7 (including water) |
Microtips
|
| Number of bores, Oryx8: |
7, 4, 3 or 2 |
| Number of bores, Oryx4: |
3 or 2 |
| Cross-section of microtip at tip |
0.45 - 0.95 mm |
| Cross-section of each bore |
150 microns I.D. |
| Dead volume |
Zero |
| Material |
Transparent flexible water repellent fluoropolymer (FEP). Protein
channel is treated to prevent the air-bubble from breaking up. |
Liquid Handling Accuracy
The CV (coefficient of variance) has been measured using 50% PEG 4000 and 95% PEG 600 (with 5% red dye) as follows.
|
| CV for 1 µl total drop volume |
3% |
| CV for 200 nl total drop volume |
5% |
| CV for 100 nl total drop volume |
6.5% |
Universal Syringe Driver
|
| Number of discrete steps for syringe volume |
More than 22,000 |
| Displacement for each step |
3.2 microns |
| Volume dispensed per step with a 100 microlitre syringe. |
5.2 nl |
| Maximum speed |
4.0 mm/second |
Accuracy of Universal Syringe
Driver |
| R.M.S. error per step |
+/- 8% |
| Nominal maximum error per step |
16% |
| Nominal maximum cumulative error over complete linear
displacement |
2 steps |
Automatic XYZV Plate Loader
|
| Linear displacement of table: |
| travel, first horizontal axis (X) |
321 mm |
| travel, second horizontal axis (Y) |
151 mm |
| travel, first vertical axis (Z) |
50 mm |
| travel, second vertical axis (V) |
52 mm |
| Nominal maximum cumulative error over complete linear
displacement |
0.1 mm |
| Length required on bench |
680 mm |
| Depth required on bench |
565 mm |
Height in extended position including
z loop |
340 mm |
| Weight |
11.8 kg |
| Time taken to dispense 96 well 1 drop experiment into e.g. SwissCI MRC 2 drop plate |
<9 min |
| Maximum speed: |
| X |
75 mm/s |
| Y |
55 mm/s |
| Z &V |
25 mm/s |
| The speed is software controllable and is fully
variable |
Chassis
|
| Width |
275 mm |
| Depth |
200 mm |
| Height |
450 mm |
| Weight |
15kg - Oryx8
8kg - Oryx4 |
No. of Chassis Units
|
| Oryx8 |
2 |
| Oryx4 |
1 |
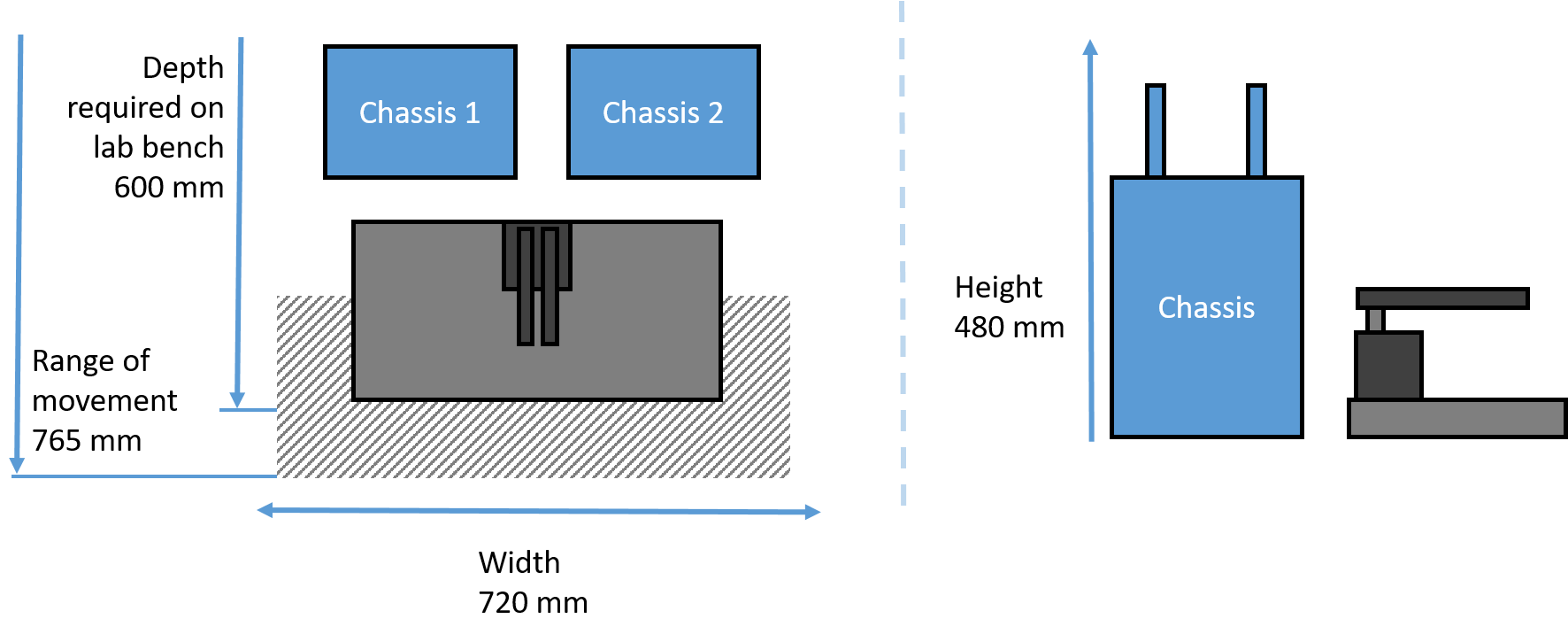
Oryx8 Minimum space required
|
Minimum space required for Oryx8 in standard configuration.
(Other configurations are possible)
|
|
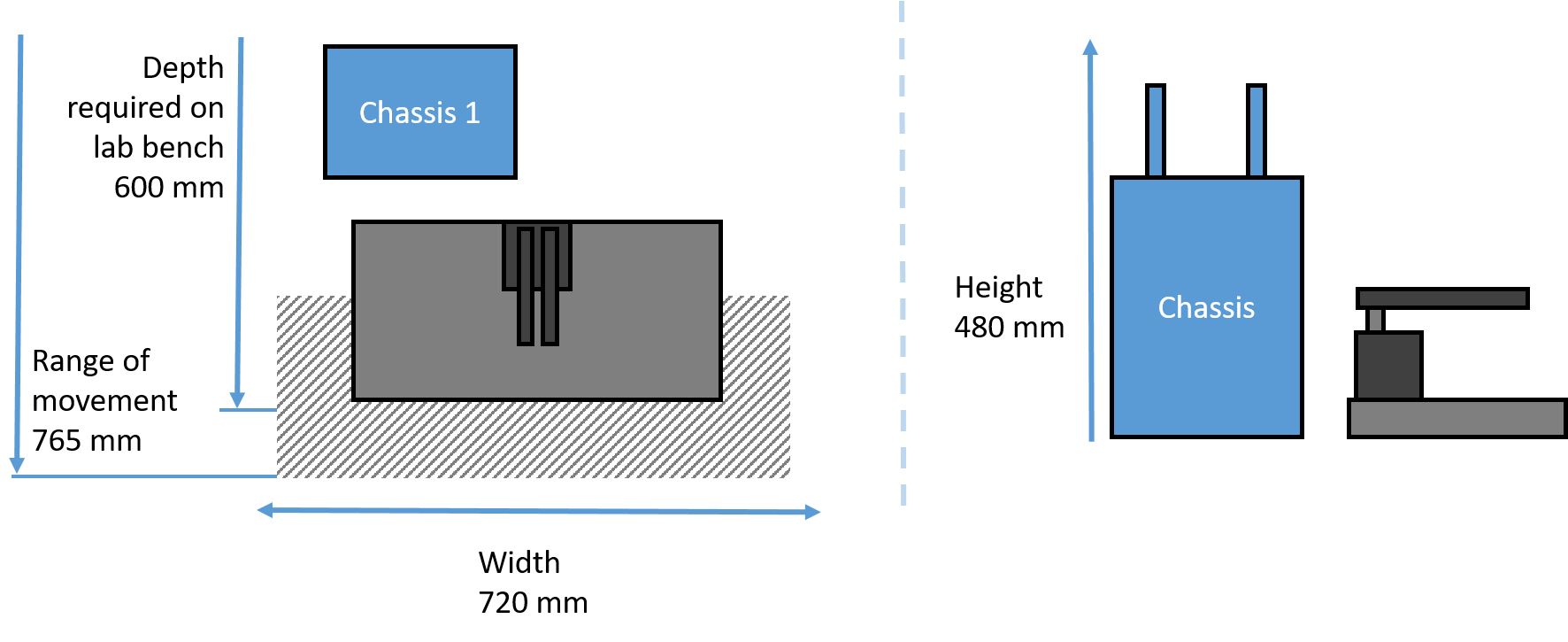
Oryx4 Minimum space required
|
Minimum space required for Oryx4 in standard configuration.
(Other configurations are possible)
|
|
